Demystifying the Federal Reserve System: Interactive Visual Guide to Monetary Policy Tools
Understanding the central banking system through powerful visualizations
The Federal Reserve System plays a pivotal role in the U.S. economy, implementing monetary policy to maintain price stability and maximum employment. This visual guide breaks down the complex mechanisms and tools used by the Fed through interactive graphics and intuitive visualizations.
Introduction to the Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System, often simply called "the Fed," serves as the central banking system of the United States. Established in 1913 through the Federal Reserve Act, it was created in response to financial panics, particularly the severe panic of 1907, which highlighted the need for a central banking authority to provide stability to the nation's monetary and financial systems.
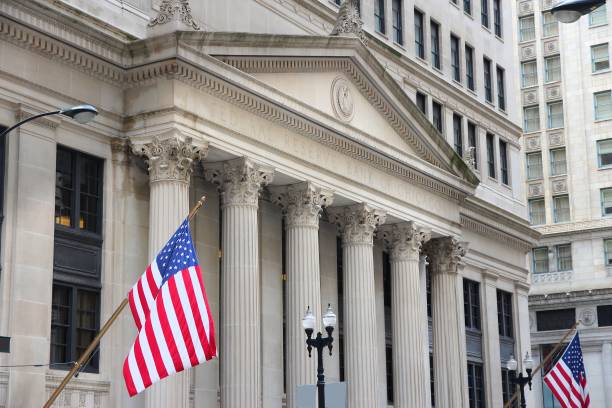

The Federal Reserve headquarters in Washington D.C., representing the central authority of U.S. monetary policy.
The Dual Mandate
Unlike many central banks that focus primarily on price stability, the Federal Reserve operates under a dual mandate established by Congress: to promote both maximum employment and stable prices. This unique responsibility requires the Fed to balance two crucial economic objectives that sometimes present tradeoffs.
The Federal Reserve's Dual Mandate
The Fed must balance two primary objectives, visualized below:
Visualizing Monetary Policy
The complexity of monetary policy operations often makes them difficult for the public to understand. Through interactive visualizations for data exploration, we can transform abstract economic concepts into intuitive visual representations that clarify how the Fed's actions impact our daily lives.
PageOn.ai's visualization tools can transform complex Federal Reserve data into intuitive visual stories, making monetary policy more accessible to students, professionals, and the general public alike. By converting intricate policy mechanisms into clear visual formats, PageOn.ai helps bridge the gap between expert knowledge and public understanding.
The Structure and Organization of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System has a unique structure that balances centralized national authority with regional input. This complex organizational design ensures that monetary policy considers economic conditions across the entire United States rather than focusing solely on major financial centers.
Federal Reserve Board of Governors
At the core of the Federal Reserve System is the Board of Governors—seven members appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate for staggered 14-year terms. This long tenure is designed to insulate the Board from political pressure and allow for long-term policy planning. The Board provides oversight and direction for the entire Federal Reserve System.
The Twelve Federal Reserve Banks
The Federal Reserve System is divided into twelve districts, each served by a regional Federal Reserve Bank. These banks implement the policies set by the Board and provide critical economic information about their regions.
Federal Reserve District Map
The United States is divided into twelve Federal Reserve districts:
graph TD
FRB[Federal Reserve Board
Washington D.C.]
FRB --> B1[District 1:
Boston]
FRB --> B2[District 2:
New York]
FRB --> B3[District 3:
Philadelphia]
FRB --> B4[District 4:
Cleveland]
FRB --> B5[District 5:
Richmond]
FRB --> B6[District 6:
Atlanta]
FRB --> B7[District 7:
Chicago]
FRB --> B8[District 8:
St. Louis]
FRB --> B9[District 9:
Minneapolis]
FRB --> B10[District 10:
Kansas City]
FRB --> B11[District 11:
Dallas]
FRB --> B12[District 12:
San Francisco]
style FRB fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style B2 fill:#FF9933,stroke:#FF8000,color:black
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York (District 2) plays a special role in implementing monetary policy.
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is the Fed's primary monetary policy-making body. It consists of all seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven Reserve Bank presidents, who serve on a rotating basis. The FOMC meets approximately eight times per year to assess economic conditions and determine appropriate monetary policy actions.

A typical Federal Open Market Committee meeting where key monetary policy decisions are discussed and made.
Using PageOn.ai's AI Blocks feature, users can create clear organizational charts that illustrate the complex reporting relationships within the Federal Reserve System. These visual aids help clarify how information flows between the Board of Governors, the regional Reserve Banks, and the FOMC, making it easier to understand how monetary policy decisions are made and implemented.
The flowchart examples available through PageOn.ai provide templates that can be adapted to show the Federal Reserve's decision-making processes, helping students and professionals alike understand the journey from economic data collection to policy implementation.
Core Monetary Policy Tools Visualized
The Federal Reserve employs several key tools to implement monetary policy and achieve its dual mandate. These instruments allow the Fed to influence interest rates, money supply, and overall credit conditions in the economy. Understanding how these tools work is essential for appreciating the Fed's role in economic management.
The Federal Funds Rate
The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight. This rate serves as a benchmark for short-term interest rates throughout the economy and is the primary tool used by the Federal Reserve to implement monetary policy, as noted on the Federal Reserve Board's educational resources.
Federal Funds Rate Historical Trend (2000-2023)
The chart shows significant rate drops during recessions (2001, 2008, 2020) and rate increases during economic expansions. Note the extended zero-rate policy following the 2008 financial crisis and the rapid increases in 2022-2023 to combat inflation.
Open Market Operations
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of securities, primarily U.S. Treasury securities, in the open market. These operations directly affect the amount of reserves in the banking system, which influences the federal funds rate.
How Open Market Operations Work
flowchart TD
FOMC[FOMC Decision] --> Directive[Policy Directive to NY Fed]
Directive --> Buy[Buy Securities]
Directive --> Sell[Sell Securities]
Buy --> IncreaseReserves[Increase Bank Reserves]
IncreaseReserves --> LowerRate[Lower Fed Funds Rate]
LowerRate --> ExpandMoney[Expansionary Policy]
Sell --> DecreaseReserves[Decrease Bank Reserves]
DecreaseReserves --> RaiseRate[Raise Fed Funds Rate]
RaiseRate --> ContractMoney[Contractionary Policy]
style FOMC fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style Buy fill:#66BB6A,stroke:#43A047,color:black
style Sell fill:#EF5350,stroke:#E53935,color:black
style ExpandMoney fill:#66BB6A,stroke:#43A047,color:black
style ContractMoney fill:#EF5350,stroke:#E53935,color:black
Reserve Requirements and Interest on Reserve Balances
Historically, reserve requirements were the amount of funds that depository institutions were required to hold in reserve against specified deposit liabilities. In March 2020, the Federal Reserve reduced reserve requirement ratios to zero percent, effectively eliminating them.
Now, the Fed primarily uses interest on reserve balances (IORB) to influence bank behavior. By paying interest on the balances that banks hold at Federal Reserve Banks, the Fed can directly affect banks' lending and borrowing decisions.
Key Monetary Policy Tools Comparison
Overnight Reverse Repurchase Facility
The overnight reverse repurchase facility (ON RRP) is a supplementary policy tool that helps control the federal funds rate. Through this facility, eligible counterparties, including money market funds, can invest funds overnight with the Federal Reserve at a specified rate, effectively establishing a floor for short-term interest rates.
This facility became particularly important as the Fed's balance sheet expanded and as regulatory changes affected short-term funding markets. The ON RRP helps prevent the federal funds rate from falling below the target range.
Overnight Reverse Repurchase Process
flowchart TD
Fed[Federal Reserve] --"1. Sells securities"--> MMF[Money Market Funds
and Other Counterparties]
MMF --"2. Pays cash"--> Fed
Fed --"3. Buys back securities
next day at higher price"--> MMF
MMF --"4. Returns securities"--> Fed
style Fed fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style MMF fill:#42A5F5,stroke:#1E88E5,color:black
The ON RRP facility allows the Fed to control short-term interest rates by offering counterparties a risk-free overnight investment option.
PageOn.ai's Deep Search capabilities can integrate real-time Federal Reserve data into dynamic visualizations, allowing users to see the most current information about these policy tools and their effects. This feature is particularly valuable for economists, financial analysts, and students who need to stay updated on monetary policy developments.
The ability to create data visualization charts that automatically update as new Federal Reserve data becomes available makes PageOn.ai an invaluable resource for monetary policy analysis and education.
Monetary Policy Implementation Through Interactive Timelines
The Federal Reserve's approach to monetary policy has evolved significantly over time, adapting to changing economic conditions and incorporating new tools and strategies. Visualizing this evolution helps us understand the Fed's current policy framework in historical context.
Key Historical Shifts in Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve's monetary policy implementation has undergone several major shifts since its founding. From the gold standard era to modern inflation targeting, these changes reflect both evolving economic understanding and responses to major economic challenges.
Evolution of Federal Reserve Monetary Policy
timeline
title Major Monetary Policy Shifts
section Early Years
1913 : Federal Reserve Act establishes the central bank
1935 : Banking Act reorganizes Fed structure
section Mid-Century
1951 : Treasury-Fed Accord gives Fed independence
1979 : Volcker focuses on controlling money supply to fight inflation
section Modern Era
1987-2006 : Greenspan era of "measured" rate adjustments
2008 : Zero interest rate policy and QE in response to financial crisis
2020 : Unprecedented pandemic response
2022 : Rapid rate increases to combat inflation
FOMC Policy Responses to Different Economic Scenarios
The Federal Open Market Committee must respond to various economic conditions, balancing its dual mandate objectives while considering global economic factors. The following visualization shows typical policy responses to different economic scenarios.
FOMC Decision-Making Framework
flowchart TD
EconData[Economic Data Analysis] --> Inflation{Inflation Trend}
EconData --> Employment{Employment Situation}
EconData --> Growth{Economic Growth}
Inflation -->|"Above Target"| HighInf[Concerns about
Price Stability]
Inflation -->|"At Target"| TargetInf[Price Stability
Maintained]
Inflation -->|"Below Target"| LowInf[Deflationary
Concerns]
Employment -->|"Strong"| HighEmp[Maximum Employment
Achieved]
Employment -->|"Weakening"| MidEmp[Employment
Concerns]
Employment -->|"Weak"| LowEmp[Far from Maximum
Employment]
Growth -->|"Strong"| HighGrowth[Robust Economy]
Growth -->|"Moderate"| MidGrowth[Stable Growth]
Growth -->|"Weak/Negative"| LowGrowth[Recessionary
Concerns]
HighInf --> PolicyChoice{Policy Decision}
TargetInf --> PolicyChoice
LowInf --> PolicyChoice
HighEmp --> PolicyChoice
MidEmp --> PolicyChoice
LowEmp --> PolicyChoice
HighGrowth --> PolicyChoice
MidGrowth --> PolicyChoice
LowGrowth --> PolicyChoice
PolicyChoice -->|"High Inflation + Strong Employment"| Tighten[Tighten Policy
Raise Rates]
PolicyChoice -->|"Low Inflation + Weak Employment"| Ease[Ease Policy
Lower Rates]
PolicyChoice -->|"Balanced Conditions"| Maintain[Maintain
Current Stance]
PolicyChoice -->|"Mixed Signals"| Gradual[Gradual
Adjustment]
style EconData fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style PolicyChoice fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style Tighten fill:#EF5350,stroke:#E53935,color:black
style Ease fill:#66BB6A,stroke:#43A047,color:black
PageOn.ai's timeline visualization tools make it easy to create interactive chronologies that reveal patterns in Federal Reserve policy changes. These timelines can be customized to highlight specific periods of interest, such as recessions, inflation surges, or major financial crises, allowing users to better understand the context of monetary policy decisions.
Mapping Connections Between Economic Indicators and Policy
Federal Reserve policy decisions are based on careful analysis of numerous economic indicators. Understanding these connections helps explain the rationale behind monetary policy shifts.
A complex network of economic indicators that influence Federal Reserve policy decisions. The visualization shows how different factors are weighted in the decision-making process.
By using line graphs to visualize trends in key economic indicators alongside Federal Reserve policy changes, PageOn.ai users can identify correlations and potential causal relationships. This type of visual analysis makes complex economic relationships more intuitive and accessible to a wide audience.
Economic Indicators and Data Visualization
The Federal Reserve monitors a vast array of economic indicators to inform its monetary policy decisions. Transforming this complex data into visual formats makes it more accessible and reveals patterns that might otherwise be difficult to discern.
GDP, Inflation, and Employment Metrics
The three most closely watched economic indicators align with the Fed's dual mandate plus overall economic health: inflation (measured by various price indices), employment (captured through labor market statistics), and GDP growth (indicating overall economic activity).
Key Economic Indicators (2023 Example)
The chart shows 2023 quarterly data for key economic indicators. Note the strong GDP growth in Q3 2023 alongside gradually declining inflation rates, presenting a mixed policy challenge for the Federal Reserve.
Money Supply Measures
The Federal Reserve tracks different measures of money supply to gauge the amount of money circulating in the economy. The two primary measures are M1 (which includes cash and checking deposits) and M2 (which includes M1 plus savings deposits, money market securities, and other time deposits).
M1 vs. M2 Money Supply Growth
The dramatic spike in M1 in 2020-2021 reflects both pandemic stimulus measures and a reclassification of certain savings deposits as transaction accounts. M2 growth was more moderate but still substantial during this period.
Currency in Circulation
Currency in circulation—the total value of U.S. currency notes and coins in the hands of the public—is another important metric monitored by the Federal Reserve. Geographic variations in currency usage can provide insights into regional economic conditions and financial inclusion.
Geographic distribution of currency in circulation across the United States, showing regional variations in cash usage.
PageOn.ai's AI-driven visualization tools can transform raw economic data into instantly understandable visual formats. These tools automatically detect the most appropriate visualization type for different metrics—using line charts for time series data like GDP growth, bar charts for comparative data like regional unemployment rates, and map data visualization basics for geographic distributions like regional banking activity.
The ability to quickly generate professional-quality visualizations from complex economic datasets makes PageOn.ai particularly valuable for economists, policymakers, journalists, and educators who need to communicate Federal Reserve data effectively.
The Transmission Mechanism of Monetary Policy
The transmission mechanism refers to the process through which monetary policy decisions affect the economy. This complex chain of effects operates through various channels, influencing interest rates, asset prices, exchange rates, and ultimately, economic output and inflation.
Monetary Policy Transmission Channels
flowchart TD
FedPolicy[Federal Reserve
Policy Decision] --> InterestRate[Interest Rate Channel]
FedPolicy --> CreditChannel[Credit Channel]
FedPolicy --> ExchangeRate[Exchange Rate Channel]
FedPolicy --> AssetPrice[Asset Price Channel]
FedPolicy --> Expectations[Expectations Channel]
InterestRate --> ShortRates[Short-term Interest Rates]
ShortRates --> LongRates[Long-term Interest Rates]
LongRates --> BorrowingCosts[Borrowing Costs]
BorrowingCosts --> Investment[Business Investment]
BorrowingCosts --> Housing[Housing Activity]
BorrowingCosts --> DurableGoods[Durable Goods Consumption]
Investment --> Aggregate[Aggregate Demand]
Housing --> Aggregate
DurableGoods --> Aggregate
Aggregate --> Output[Economic Output]
Output --> Employment[Employment]
Output --> Inflation[Inflation]
style FedPolicy fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style Aggregate fill:#42A5F5,stroke:#1E88E5,color:black
style Output fill:#66BB6A,stroke:#43A047,color:black
style Inflation fill:#EF5350,stroke:#E53935,color:white
This diagram shows the primary interest rate channel, but other channels (credit, exchange rate, asset price, expectations) also play important roles in the transmission process.
Time-Lag Visualizations
One of the most challenging aspects of monetary policy is that its effects are not immediate. Different sectors of the economy respond to policy changes with varying time lags, making it difficult to gauge the full impact of policy actions in real time.
Monetary Policy Time Lags by Sector
This time lag challenge is why the Federal Reserve must be forward-looking in its policy decisions, basing them on economic forecasts rather than current conditions alone. The policy implemented today is intended to address economic conditions 6-18 months in the future.
Ripple Effects Throughout the Economy
Monetary policy changes create ripple effects that spread throughout the economy, often with different intensities across various sectors and demographic groups. Understanding these differential impacts is crucial for comprehensive policy evaluation.

Visualization of how monetary policy changes ripple through different sectors of the economy with varying intensities and timing.
PageOn.ai's visualization capabilities can translate abstract economic concepts into concrete visual narratives. By creating animated sequences that show how policy changes propagate through the economy over time, PageOn.ai helps users understand the dynamic nature of monetary policy effects. These visualizations can be particularly valuable for educational purposes, helping students grasp complex economic relationships that are difficult to convey through text alone.
Case Studies: Visualizing Historical Monetary Policy Responses
Examining historical monetary policy responses to major economic challenges provides valuable insights into the evolution of the Federal Reserve's toolkit and decision-making processes. These case studies highlight how the Fed has adapted its approach in response to different types of economic crises.
The 2007-2009 Financial Crisis
The 2007-2009 global financial crisis forced the Federal Reserve to deploy both conventional and unconventional monetary policy tools. After rapidly cutting the federal funds rate to near zero, the Fed introduced new facilities to provide liquidity to financial markets and implemented large-scale asset purchase programs (quantitative easing) to further stimulate the economy.
Federal Reserve Balance Sheet Expansion During Financial Crisis
The chart illustrates the dramatic expansion of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet during and after the financial crisis, reflecting the implementation of quantitative easing programs.
Quantitative Easing Programs
Quantitative easing (QE) involves large-scale asset purchases by the Federal Reserve to lower long-term interest rates and provide additional monetary stimulus when short-term rates are already at or near zero. The Fed implemented three major rounds of QE following the financial crisis, each with different characteristics and market impacts.
| Program | Period | Assets Purchased | Approximate Size | Primary Objective |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QE1 | Nov 2008 - Mar 2010 | Agency MBS, agency debt, Treasuries | $1.75 trillion | Support mortgage market, address financial crisis |
| QE2 | Nov 2010 - Jun 2011 | Treasury securities | $600 billion | Strengthen recovery, prevent deflation |
| Operation Twist | Sep 2011 - Dec 2012 | Sell short-term Treasuries, buy long-term Treasuries | $667 billion | Lower long-term rates without expanding balance sheet |
| QE3 | Sep 2012 - Oct 2014 | Agency MBS, Treasury securities | $85 billion monthly (open-ended) | Support housing market, reduce unemployment |
COVID-19 Pandemic Response
The Federal Reserve's response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 was unprecedented in both scale and scope. It included cutting the federal funds rate to near zero, reintroducing crisis-era liquidity facilities, establishing new emergency lending programs, and conducting massive asset purchases at a pace far exceeding previous QE programs.
Federal Reserve COVID-19 Response
flowchart TB
Fed[Federal Reserve
COVID-19 Response] --> Rate[Federal Funds Rate
Cut to 0-0.25%]
Fed --> QE[Quantitative Easing
Treasury & MBS Purchases]
Fed --> Swap[Central Bank
Swap Lines]
Fed --> Facilities[Emergency
Credit Facilities]
Facilities --> PMCCF[Primary Market
Corporate Credit Facility]
Facilities --> SMCCF[Secondary Market
Corporate Credit Facility]
Facilities --> MLF[Municipal
Liquidity Facility]
Facilities --> MSLP[Main Street
Lending Program]
Facilities --> PPPLF[Paycheck Protection
Program Liquidity Facility]
style Fed fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style Rate fill:#FF9933,stroke:#FF8000,color:black
style QE fill:#FF9933,stroke:#FF8000,color:black
style Facilities fill:#42A5F5,stroke:#1E88E5,color:black
The diagram illustrates the multi-faceted approach of the Federal Reserve's COVID-19 response, which included both traditional tools and innovative new facilities.
PageOn.ai's data visualization capabilities make it possible to create rich visual stories that explain complex policy decisions. For example, by incorporating Federal Reserve data, policy announcements, and market reactions into a single interactive timeline, PageOn.ai can help users understand the context, implementation, and effects of monetary policy responses during historical crises.
The Global Impact of Federal Reserve Decisions
The Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions reverberate far beyond U.S. borders, affecting international markets, exchange rates, and global capital flows. As the issuer of the world's primary reserve currency, the Fed's actions have outsized influence on the global financial system.
Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Changes in Federal Reserve policy can drive significant movements in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies. When the Fed raises interest rates, higher yields on dollar-denominated assets often attract foreign capital, strengthening the dollar—and vice versa when rates are cut.
U.S. Dollar Index Response to Fed Policy Changes
The chart shows the relationship between the Federal Reserve's interest rate policy and the strength of the U.S. dollar against a basket of foreign currencies. Note the dollar's strengthening during rate hiking cycles in 2017-2018 and 2022-2023.
Global Financial Flows
Changes in Federal Reserve policy affect the direction and volume of global capital flows. When the Fed tightens policy, emerging markets often experience capital outflows as investors redirect funds to higher-yielding U.S. assets. Conversely, looser Fed policy can trigger capital inflows to emerging markets as investors search for higher returns.
Visualization of global capital flows responding to Federal Reserve policy tightening, showing outflows from emerging markets to the United States.
Central Bank Coordination
Major central banks—including the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, Bank of Japan, and Bank of England—sometimes coordinate their policy actions, especially during global crises. This coordination is designed to maximize policy effectiveness and minimize market disruptions.
Major Central Bank Policy Rates Comparison
This comparison illustrates how different central banks adjust their policy rates over time, sometimes in coordination (as in the 2020 pandemic response) and sometimes divergently (as in 2023 when the Bank of Japan maintained ultra-loose policy while others tightened).
PageOn.ai's visualization capabilities are particularly useful for demonstrating global economic interconnectedness. By creating interactive maps that show how Federal Reserve policy changes affect different countries and regions, PageOn.ai helps users understand the complex web of international financial relationships and dependencies.
Future Trends and Digital Tools for Monetary Policy Education
The field of monetary policy communication and education is evolving rapidly, with new technologies enabling more interactive, personalized, and accessible ways to understand the Federal Reserve's actions and their economic impacts.
Emerging Visualization Technologies
Advanced visualization technologies—including augmented reality, virtual reality, and interactive 3D modeling—are creating new possibilities for monetary policy education. These tools can transform abstract economic concepts into immersive experiences that make complex relationships more intuitive and memorable.

Concept visualization of an augmented reality interface for exploring Federal Reserve data and policy decisions interactively.
Interactive Simulations
Interactive simulations that allow users to explore different policy scenarios and their potential outcomes are becoming powerful educational tools. These simulations can help students, policymakers, and the general public better understand the tradeoffs and challenges involved in monetary policy decisions.
Monetary Policy Simulation Framework
flowchart TD
Input[User Inputs
Policy Parameters] --> Model[Economic Model
Processes Inputs]
Model --> Output[Simulation Generates
Economic Outcomes]
Output --> Visualization[Interactive Visualization
of Results]
Visualization --> Comparison[Comparison with
Historical Scenarios]
Visualization --> Feedback[Feedback on
Policy Effectiveness]
Feedback --> Adjustment[Suggested Parameter
Adjustments]
Adjustment --> Input
style Input fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style Model fill:#42A5F5,stroke:#1E88E5,color:black
style Output fill:#66BB6A,stroke:#43A047,color:black
style Visualization fill:#EF5350,stroke:#E53935,color:white
A conceptual framework for interactive monetary policy simulations, showing the cyclical process of policy experimentation and learning.
The Role of AI in Monetary Policy Transparency
Artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly important role in making monetary policy more transparent and accessible. AI-powered tools can analyze Federal Reserve communications, extract key insights, and present them in user-friendly formats tailored to different audience needs.
AI Applications in Monetary Policy Communication
Customizable Dashboards
Customizable dashboards that allow users to track specific monetary policy indicators according to their interests and needs are becoming increasingly sophisticated. These dashboards can combine data from multiple sources, update in real-time, and generate insights tailored to different user types, from financial professionals to students.
PageOn.ai excels at transforming complex Federal Reserve publications into engaging visual content. By automatically extracting key information from dense policy documents, research papers, and economic reports, PageOn.ai makes it possible to create clear, visually compelling summaries that highlight the most important points without requiring users to wade through technical jargon and complicated data tables.
Example of a customizable dashboard for tracking monetary policy indicators, created using PageOn.ai's visualization tools.
Educational Resources and Interactive Learning Tools
The Federal Reserve System offers a wealth of educational resources designed to help students, teachers, and the general public understand monetary policy and central banking. These resources range from basic explanations to sophisticated interactive tools for advanced learning.
Federal Reserve Educational Resources
The Federal Reserve provides numerous educational materials through its websites, including interactive tools like the ones featured in the Federal Reserve's interactive data visualizations. These resources include lesson plans, videos, publications, and games designed to teach economic and financial concepts at various educational levels.

Overview of educational resources provided by the Federal Reserve System for different audiences and learning levels.
Building Custom Visualizations for Classroom Use
Educators can create customized visualizations to help students understand monetary policy concepts. These visualizations can be tailored to specific learning objectives, student levels, and classroom contexts.
Visualization Types for Different Learning Objectives
This chart shows which visualization types work best for different monetary policy learning objectives, helping educators select the most effective visual formats for their specific teaching goals.
Step-by-Step Tutorial for Creating Monetary Policy Infographics
Creating effective infographics about monetary policy requires a thoughtful process that begins with identifying key concepts and determining the most appropriate visual representations. The following steps outline a methodology for developing clear, informative monetary policy infographics:
Infographic Creation Process
flowchart LR
Define[1. Define
Learning Objective] --> Research[2. Research
Content]
Research --> Identify[3. Identify Key
Data Points]
Identify --> Structure[4. Structure
Information Hierarchy]
Structure --> Visual[5. Choose
Visual Format]
Visual --> Design[6. Create
Draft Design]
Design --> Test[7. Test with
Target Audience]
Test --> Refine[8. Refine Based
on Feedback]
style Define fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF6000,color:white
style Visual fill:#42A5F5,stroke:#1E88E5,color:black
style Test fill:#66BB6A,stroke:#43A047,color:black
A systematic process for creating effective monetary policy infographics, emphasizing audience needs and iterative design.
Connecting Visualization Techniques to Economic Literacy
Visual literacy and economic literacy are increasingly interconnected in our data-rich world. Effective visualization techniques can significantly enhance understanding of complex economic concepts, making them more accessible and memorable for various audiences.
PageOn.ai can help develop personalized learning materials about the Federal Reserve tailored to different educational levels and learning objectives. By transforming complex economic data into clear, engaging visualizations, PageOn.ai makes monetary policy concepts more accessible to students, professionals, and the general public.

A personalized learning module about Federal Reserve monetary policy created with PageOn.ai, featuring adaptive content based on the user's knowledge level.
Transform Your Visual Expressions with PageOn.ai
Bring monetary policy concepts to life with stunning visualizations that make complex economic ideas instantly understood. PageOn.ai's powerful tools help you create professional-quality graphics, interactive charts, and dynamic diagrams without specialized design skills.
Start Creating with PageOn.ai TodayYou Might Also Like
How to Design Science Lesson Plans That Captivate Students
Create science lesson plans that captivate students with hands-on activities, clear objectives, and real-world applications to foster curiosity and critical thinking.
How to Write a Scientific Review Article Step by Step
Learn how to write a review article in science step by step. Define research questions, synthesize findings, and structure your article for clarity and impact.
How to Write a Self-Performance Review with Practical Examples
Learn how to write a self-performance review with examples and tips. Use an employee performance review work self evaluation sample essay to guide your process.
How to Write a Spec Sheet Like a Pro? [+Templates]
Learn how to create a professional spec sheet with key components, step-by-step guidance, and free templates to ensure clarity and accuracy.
