Legal Interpretation Theory: From Textual Analysis to Constructive Meaning-Making
Bridging traditional legal frameworks with innovative visual approaches to transform complex interpretation into clear understanding
I've spent years navigating the complex terrain of legal interpretation, watching as the field has evolved from rigid textualism toward more nuanced approaches that recognize interpretation as an act of meaning creation. Throughout my journey, I've observed how the inability to visualize abstract legal concepts often creates barriers to understanding and application.
In this exploration, we'll trace the evolution of legal interpretation theory, examining how the field has expanded beyond pure textual analysis to embrace constructivist approaches that acknowledge the creative aspects of interpretation. More importantly, I'll demonstrate how visual tools can transform abstract legal theories into tangible frameworks that bridge competing interpretive schools and enhance practical application.

As we journey through the theoretical landscape of legal interpretation, we'll discover how visualization tools like those offered by symbols and meanings systems can bridge the gap between abstract theory and practical application, making complex legal reasoning more accessible to practitioners, students, and clients alike.
The Evolution of Legal Interpretation Frameworks
I've watched legal interpretation transform dramatically over the centuries. What began as a strict adherence to text has evolved into a rich tapestry of interpretive approaches that recognize the inherently constructive nature of meaning-making in law.
timeline
title Evolution of Legal Interpretation Approaches
section Historical
Strict Textualism : Literal reading of text only
Intentionalism : Focus on legislative intent
section Modern
Purposivism : Emphasis on law's purpose
Pluralistic Approaches : Multiple interpretive tools
section Contemporary
Constructivism : Recognition of meaning-making
Visual Integration : Technology-enhanced interpretation
The historical shift from strict textualism to more dynamic approaches reflects a growing recognition that legal interpretation is not merely about discovering pre-existing meaning but involves an active process of construction. As Stanford's Encyclopedia of Philosophy on Legal Interpretation notes, modern judges and legal scholars often embrace pluralistic approaches that combine textual, purposive, historical, and precedent-based reasoning.
In my experience, this evolution has created both opportunities and challenges. While pluralistic approaches allow for more nuanced interpretation, they also introduce complexity that can be difficult to navigate without proper tools.
Comparing Traditional and Modern Interpretive Approaches
The visualization above illustrates how modern approaches incorporate multiple dimensions of interpretation compared to traditional textualism. This evolution toward pluralism creates a perfect opportunity for visual tools to help legal professionals integrate these diverse interpretive elements into coherent analytical frameworks.
Foundations of Textual Analysis in Legal Interpretation
Despite the evolution toward more pluralistic approaches, textual analysis remains the cornerstone of legal interpretation. I've found that understanding the methodologies of textual analysis is essential before moving to more constructive approaches.
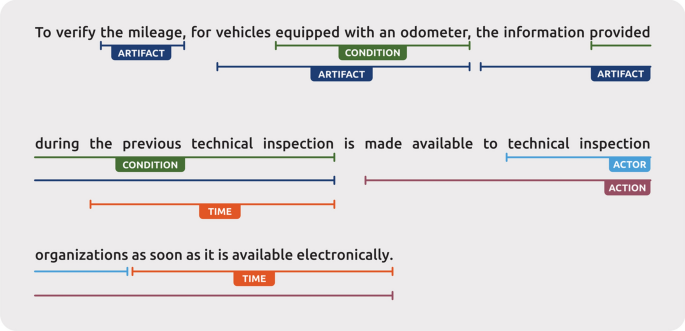
Textual analysis in legal contexts involves several distinct methodologies, each with its own strengths and limitations. According to specialists in legal method and writing, effective textual analysis requires examining legal documents using various techniques to understand their meaning and implications.
Key Textual Analysis Methodologies
- Plain Meaning Rule: Words are interpreted according to their ordinary, dictionary meaning
- Semantic Canons: Rules about language usage that guide interpretation
- Syntactic Canons: Rules about grammatical structure and its legal implications
- Contextual Reading: Understanding terms within their textual surroundings
- Whole Text Analysis: Ensuring interpretations are consistent throughout the document
A critical distinction exists between textualism in statutory interpretation and "public meaning" originalism in constitutional interpretation. While both prioritize text, they differ in how they approach historical context and evolution of meaning over time.
flowchart TD
A[Legal Text] --> B{Interpretive Approach}
B -->|Textualism| C[Focus on Contemporary
Understanding of Words]
B -->|Public Meaning
Originalism| D[Focus on Original
Public Understanding]
C --> E[Statutory
Interpretation]
D --> F[Constitutional
Interpretation]
C --> G[Dictionary
Definitions]
C --> H[Linguistic
Canons]
D --> I[Historical
Dictionaries]
D --> J[Contemporary
Documents]
style A fill:#FF8000,color:white
style B fill:#FF8000,color:white
One of the most significant challenges in textual analysis is language precision. Legal documents often contain terms with specialized meanings that may differ from everyday usage, creating ambiguities that must be resolved through careful analysis.
In my practice, I've found that PageOn.ai's AI Blocks provide an exceptional tool for mapping textual relationships and linguistic patterns in legal documents. By visualizing these connections, we can identify patterns and inconsistencies that might be missed in traditional textual analysis, creating a bridge to more constructive interpretive approaches.
Beyond the Text: Constructivist Approaches to Legal Interpretation
Throughout my career, I've witnessed a significant shift toward constructivist theories that view interpretation as an act of meaning creation rather than mere discovery. These approaches acknowledge that interpreters don't simply extract pre-existing meaning from texts; they actively construct meaning through their interpretive process.
Constructivist approaches recognize that context shapes legal meaning beyond the literal text. This includes historical context, the purpose of the law, societal values, and practical consequences of different interpretations.
Elements of Constructivist Legal Interpretation
Lifante Vidal's constructivist conception of legal interpretation offers a particularly insightful framework. Her approach emphasizes that interpretation is not merely about discovering meaning but about constructing it within appropriate constraints. This process involves balancing fidelity to text with recognition of the inherently creative nature of interpretation.
In examining constructivist approaches, I've found that evolution of law visualization techniques can illuminate how meaning has been constructed differently across historical periods and jurisdictions. These visual tools reveal patterns that might otherwise remain obscured in purely textual analysis.
PageOn.ai's Deep Search functionality provides an exceptional tool for integrating diverse contextual elements into visual legal frameworks. By mapping relationships between text, context, purpose, and consequences, we can create more comprehensive interpretive models that honor the constructivist nature of legal interpretation.
Cognitive Dimensions of Legal Interpretation
In my work with legal interpretation, I've become increasingly aware of how cognitive processes fundamentally shape how we derive meaning from legal texts. Kahneman's dual-process theory provides a valuable framework for understanding these dynamics.
flowchart TB
A[Legal Interpretation Process]
A --> B[System 1 Thinking]
A --> C[System 2 Thinking]
B --> D[Fast]
B --> E[Intuitive]
B --> F[Automatic]
B --> G[Pattern Recognition]
C --> H[Slow]
C --> I[Deliberate]
C --> J[Analytical]
C --> K[Logical Reasoning]
L[Cognitive Biases]
L --> M[Confirmation Bias]
L --> N[Anchoring]
L --> O[Availability Heuristic]
M --> P[Affects Legal Interpretation]
N --> P
O --> P
style A fill:#FF8000,color:white
style B fill:#42A5F5,color:white
style C fill:#66BB6A,color:white
style L fill:#FF5252,color:white
System 1 thinking—fast, intuitive, and automatic—often drives our initial reactions to legal texts. Meanwhile, System 2 thinking—slow, deliberate, and analytical—allows for more careful consideration of interpretive options. Legal interpretation requires a balance between these cognitive modes.

Cognitive biases pose significant challenges to legal interpretation. Confirmation bias leads us to favor interpretations that align with our pre-existing beliefs. Anchoring causes us to rely too heavily on initial information. The availability heuristic makes recent or memorable cases disproportionately influence our interpretations.
Cognitive Biases in Legal Interpretation
- Confirmation Bias: Tendency to search for and favor information that confirms pre-existing beliefs
- Anchoring: Over-reliance on the first piece of information encountered
- Availability Heuristic: Overemphasizing easily recalled examples
- Status Quo Bias: Preference for established interpretations
- Authority Bias: Giving excessive weight to interpretations from prestigious sources
I've found that visual tools can effectively bypass many cognitive limitations in complex legal analysis. By externalizing our thinking processes and making them visible, we can identify biases and logical gaps that might otherwise go unnoticed.
PageOn.ai's Vibe Creation feature offers a powerful way to transform complex cognitive frameworks into accessible visual models. By creating visual representations of interpretive processes, we can better understand how different cognitive factors influence our legal reasoning and develop more robust interpretive approaches.
Bridging Interpretive Schools Through Visual Representation
The ongoing debate between textualism, intentionalism, and purposivism has dominated legal interpretation discourse for decades. In my experience, these approaches are often presented as mutually exclusive, creating unnecessary divisions in legal practice.

Visual tools offer a unique opportunity to reveal commonalities and differences between competing interpretive approaches. By mapping these approaches visually, we can identify points of convergence and divergence, creating opportunities for more integrated interpretive methods.
Comparing Major Interpretive Schools
Visualization can integrate multiple interpretive lenses simultaneously, allowing legal professionals to consider text, intent, purpose, and consequences in a more holistic manner. This integration is particularly valuable when dealing with complex or ambiguous legal questions.
I've found that AI legal assistants can be particularly helpful in creating these integrative visual models. By processing large volumes of legal text and identifying patterns across different interpretive approaches, AI tools can help legal professionals develop more nuanced and comprehensive interpretations.
PageOn.ai provides dynamic visual modeling capabilities that show how different interpretive methods yield varying outcomes. These models allow legal professionals to test multiple interpretive approaches simultaneously, identifying which approach or combination of approaches best serves the needs of justice in a particular case.
From Theory to Practice: Visualizing Legal Interpretation in Action
Moving from abstract theory to practical application has always been one of the greatest challenges in legal interpretation. In my practice, I've found that case studies provide invaluable insights into how different interpretive approaches play out in real-world scenarios.
flowchart TD
A[Landmark Case: District of Columbia v. Heller] --> B{Interpretive Approaches}
B --> C[Textualist Approach]
B --> D[Originalist Approach]
B --> E[Living Constitution Approach]
C --> F[Focus on Second Amendment Text]
D --> G[Focus on Original Public Meaning]
E --> H[Focus on Contemporary Context]
F --> I[Analysis of "right of the people"]
F --> J[Analysis of "keep and bear Arms"]
F --> K[Analysis of "well regulated Militia"]
G --> L[Historical Documents]
G --> M[Contemporary Dictionaries]
G --> N[Founding Era Practices]
H --> O[Modern Gun Violence]
H --> P[Public Safety Concerns]
H --> Q[Technological Changes]
I --> R[Majority Opinion]
J --> R
K --> R
L --> R
M --> R
O --> S[Dissenting Opinion]
P --> S
Q --> S
style A fill:#FF8000,color:white
style B fill:#FF8000,color:white
style R fill:#66BB6A,color:white
style S fill:#FF5252,color:white
Landmark cases like District of Columbia v. Heller demonstrate how interpretive methodology significantly impacts outcomes. In Heller, the majority's textualist and originalist approach led to recognition of an individual right to bear arms, while the dissent's more purposive and living constitution approach emphasized public safety concerns.
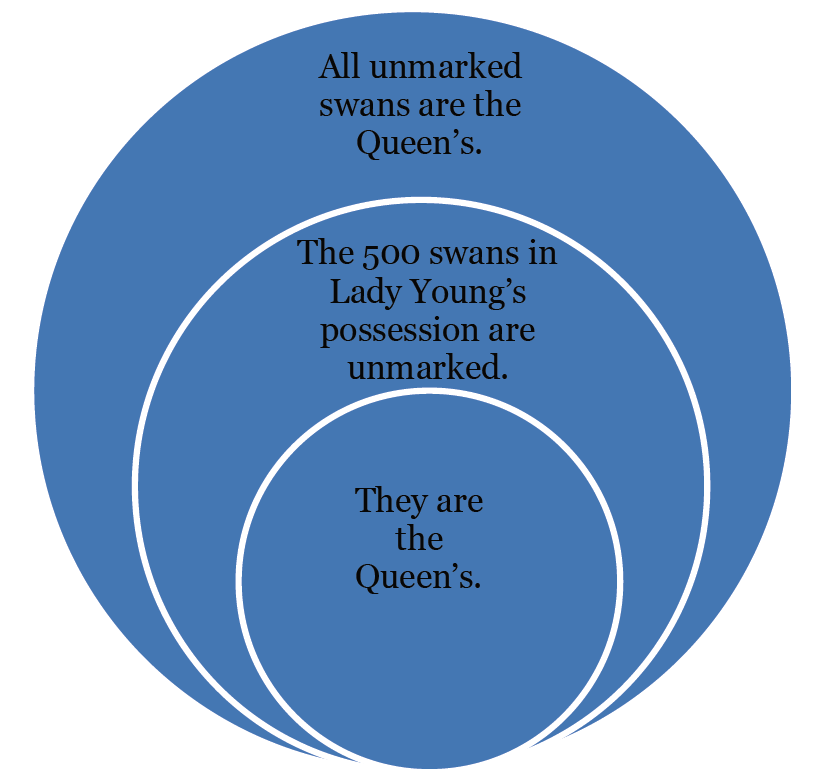
Transforming abstract legal reasoning into clear visual narratives requires identifying key decision points and interpretive moves. By mapping these elements visually, we can better understand how different interpretive approaches lead to different outcomes.
AI ChatGPT prompts for legal writing can help legal professionals generate initial visualizations of interpretive approaches, which can then be refined and customized to specific cases. These tools are particularly valuable for quickly testing multiple interpretive frameworks against complex fact patterns.
I've found that PageOn.ai's Agentic capabilities offer powerful tools for transforming complex legal theories into actionable visual frameworks. By creating interactive visualizations that allow users to explore different interpretive paths, legal professionals can develop more nuanced and effective arguments that integrate multiple interpretive approaches.
The Future of Legal Interpretation: AI-Enhanced Visual Meaning-Making
As I look toward the future of legal interpretation, I see AI tools fundamentally transforming how we approach the meaning-making process. These technologies are not replacing traditional interpretive methods but enhancing them in ways that make them more accessible, transparent, and effective.

Emerging methodologies are combining traditional legal analysis with visual meaning-making in innovative ways. These approaches leverage AI to process vast amounts of legal text while using visualization to make patterns and relationships more apparent to human interpreters.
AI-Enhanced Legal Interpretation Methods
Ethical considerations in AI-assisted legal interpretation require careful attention. Issues of transparency, bias, accountability, and human oversight must be addressed to ensure that these tools enhance rather than undermine justice. Legal professionals must maintain ultimate responsibility for interpretive decisions while leveraging AI to expand their analytical capabilities.
Visual understanding medical law demonstrates how specialized legal domains can benefit from visual interpretation tools. Similar approaches can be applied across all legal specialties, making complex legal concepts more accessible to practitioners, clients, and the public.
Looking ahead, I believe PageOn.ai's integration of visual thinking with legal analysis will reshape interpretive practices throughout the legal profession. By making the interpretive process more transparent, collaborative, and accessible, these tools will help legal professionals develop more robust, nuanced, and just interpretations of the law.
Transform Your Legal Interpretation with PageOn.ai
Move beyond traditional text-based analysis and discover how visual tools can enhance your legal reasoning, clarify complex interpretations, and communicate more effectively with clients and colleagues.
Start Visualizing Legal Concepts TodayConclusion: The Visual Future of Legal Interpretation
Throughout this exploration of legal interpretation theory, I've demonstrated how the field has evolved from strict textualism toward more constructive approaches that recognize interpretation as an act of meaning creation. The integration of visual tools into this process represents the next frontier in legal interpretation.
By bridging textual analysis and constructive meaning-making through visual representation, legal professionals can develop more nuanced, transparent, and effective interpretive approaches. These visual tools make complex legal reasoning more accessible to all stakeholders in the legal process.
As AI continues to transform legal practice, the integration of visual thinking with traditional legal analysis will become increasingly important. PageOn.ai stands at the forefront of this transformation, offering tools that enhance interpretive capabilities while maintaining the human judgment essential to just legal outcomes.
I invite you to explore how visual tools can transform your approach to legal interpretation, making complex legal concepts more accessible, your reasoning more transparent, and your arguments more persuasive. The future of legal interpretation is visual, and that future is already here.
You Might Also Like
Bridging Worlds: How Diffusion Models Are Reshaping Language Generation | PageOn.ai
Explore the revolutionary convergence of diffusion models and language generation. Discover how diffusion techniques are creating new paradigms for NLP, bridging visual and linguistic domains.
Visualizing the AI Revolution: From AlphaGo to AGI Through Key Visual Milestones
Explore the visual journey of AI evolution from AlphaGo to AGI through compelling timelines, infographics and interactive visualizations that map key breakthroughs in artificial intelligence.
First Principles Framework for Building Powerful AI Commands | Master AI Prompt Engineering
Learn the first principles approach to crafting powerful AI commands. Master prompt engineering with proven frameworks, templates, and visualization techniques for optimal AI interaction.
Creating Visual AI Ethics Frameworks: A Leadership Guide for Modern Business | PageOn.ai
Discover how to develop comprehensive visual AI ethics frameworks for your organization. This guide helps business leaders translate complex ethical principles into clear visual guidelines.
