Visualizing the CIA Triad: A Modern Framework for Cybersecurity Success
A comprehensive guide to understanding and implementing the foundation of information security
In today's increasingly complex digital landscape, cybersecurity has become a critical priority for organizations of all sizes. As I've worked with companies across various industries, I've found that having a clear, foundational framework is essential for building robust security practices. The CIA triad provides exactly that foundation—a time-tested model that continues to guide effective security strategies even as technologies evolve.
Throughout this guide, I'll walk you through each component of the CIA triad, showing how these principles can be visualized and implemented in modern security architectures. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to balance and apply these principles to strengthen your organization's security posture.
Demystifying the CIA Triad Foundation
The CIA triad is an information security model that forms the cornerstone of most security programs and policies. Despite its name, it has nothing to do with the Central Intelligence Agency—rather, CIA stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These three principles provide a framework for thinking about different aspects of information security and how they interact.
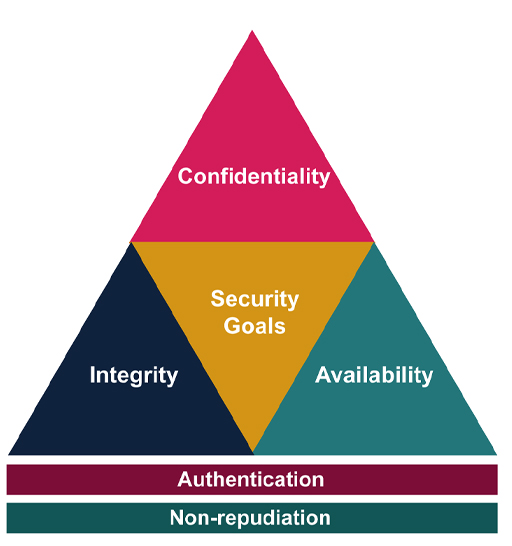
The Three Core Pillars
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that information is accessible only to those authorized to access it.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy, consistency, and trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle.
- Availability: Ensuring that information and systems are accessible to authorized users when needed.
Historical Development
The CIA triad model developed organically over time, with roots in early computing and academic papers from the 1970s and 1980s. While no single person is credited with its creation, the model has evolved to become a universally accepted standard in information security. It provides organizations with a clear framework to evaluate their security posture and identify potential vulnerabilities.
Evolution of the CIA Triad
Below is a timeline showing how the CIA triad has evolved over the decades:
timeline
title Evolution of the CIA Triad
1970s : Early security concepts emerge in computing
1970s : Focus on access control and data protection
1980s : Academic papers formalize security principles
1980s : CIA components begin to take shape
1990s : CIA triad becomes recognized security model
2000s : Wide adoption in security frameworks
2010s : Adaptation for cloud computing
2020s : Extension for AI and IoT environments
I've found that while the CIA triad is conceptually simple, translating these abstract principles into tangible security measures can be challenging. This is where visual representations become invaluable. Using PageOn.ai's visual approach, I can transform these abstract security concepts into clear, actionable visuals that help teams better understand and implement security measures across an organization.
As we explore each pillar in detail, we'll see how these principles work together to create a comprehensive security strategy that protects your most valuable assets while enabling your business to function effectively.
Confidentiality: Protecting Sensitive Information
Confidentiality is perhaps the most recognizable aspect of information security for most people. It's about ensuring that sensitive data is accessible only to authorized individuals and systems. When I work with organizations to enhance their security posture, confidentiality is often their primary concern—particularly for those handling personal data, financial information, or intellectual property.
Core Principles of Confidentiality
At its heart, confidentiality revolves around two key concepts: information access control and data privacy. Access control determines who can view, modify, or use specific information, while data privacy focuses on protecting personal information from unauthorized access and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Visualizing Confidentiality Breaches
The impact of confidentiality breaches across different organizational aspects:
Key Implementation Strategies
Authentication Mechanisms
Multi-factor authentication, biometrics, and single sign-on solutions that verify user identity before granting access to protected resources.
Encryption Protocols
Data encryption at rest and in transit, using standards like AES, RSA, and TLS to protect information from unauthorized access.
Access Management Systems
Role-based access control, least privilege principles, and regular access reviews to ensure appropriate permissions.
Authentication Flow
A visual representation of a secure multi-factor authentication process:
flowchart TD
A[User Access Request] --> B{Credential Check}
B -->|Valid| C[Send MFA Challenge]
B -->|Invalid| D[Access Denied]
C --> E{Verify MFA}
E -->|Valid| F[Check Authorization]
E -->|Invalid| G[Access Denied]
F -->|Authorized| H[Grant Access]
F -->|Unauthorized| I[Access Denied]
style A fill:#FF8000,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style H fill:#4DFFB8,stroke:#fff,color:#333
style D fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style G fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style I fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
When working with organizations to implement confidentiality measures, I've found that visualizing data flows and access points is crucial. Using PageOn.ai's AI Blocks, I can map confidentiality relationships across organizational data, making it easier to identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure comprehensive protection.
By creating visual maps of sensitive data locations and access patterns, teams can better understand where to focus their security efforts and how different protection mechanisms work together to maintain confidentiality across the organization.
Integrity: Ensuring Data Accuracy and Trustworthiness
Data integrity is about maintaining and assuring the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its entire lifecycle. In my experience, integrity often receives less attention than confidentiality in initial security planning, but its importance cannot be overstated. Without integrity, you might be protecting data that's already been compromised or corrupted—rendering your confidentiality measures somewhat meaningless.

Definition and Importance
Integrity ensures that data remains unchanged during storage, transmission, and processing. It guarantees that information hasn't been modified by unauthorized users, whether accidentally or deliberately. This principle is particularly critical for financial data, medical records, and operational systems where accuracy directly impacts decision-making and safety.
Data Integrity Components
The key elements that contribute to maintaining data integrity:
Implementation Approaches
Integrity Verification Process
A flowchart showing how data integrity is verified using hash functions:
flowchart TD
A[Original Data] -->|Generate| B[Hash Value A]
C[Transmitted/Stored Data] -->|Generate| D[Hash Value B]
B --> E{Compare Hashes}
D --> E
E -->|Match| F[Data Integrity Verified]
E -->|No Match| G[Data Integrity Compromised]
style A fill:#A64DFF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style C fill:#A64DFF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style F fill:#4DFFB8,stroke:#fff,color:#333
style G fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
Checksums & Hash Functions
Mathematical algorithms like SHA-256 that create unique fingerprints of data to detect unauthorized changes.
Digital Signatures
Cryptographic techniques that verify both data integrity and authenticity by confirming the sender's identity.
Version Control Systems
Tools that track changes to files over time, providing audit trails and the ability to revert to previous states.
In my work with financial institutions, I've seen how critical integrity verification workflows are for maintaining trust. Using PageOn.ai's structural visualization tools, I can create clear visual representations of integrity processes that help teams understand how data is protected throughout its lifecycle.
These visualizations have proven particularly valuable for training new team members and communicating with non-technical stakeholders about the importance of integrity controls. By showing how each verification step contributes to overall data trustworthiness, we can foster a culture that prioritizes integrity alongside other security concerns.
Availability: Guaranteeing Reliable Access
Availability ensures that information and systems are accessible to authorized users when they need them. This third pillar of the CIA triad is often overlooked until a system goes down, but I've found it's just as crucial as the other two components. After all, what good is secure, accurate information if it can't be accessed when needed?

Critical Components of System Availability
Availability encompasses everything from system uptime and performance to disaster recovery and business continuity. It requires planning for both routine maintenance and unexpected disruptions, ensuring that systems can recover quickly from failures with minimal impact on users.
Common Availability Threats
Distribution of different types of availability threats faced by organizations:
Implementation Strategies
Load Balancing Architecture
A visual representation of how load balancing improves availability:
flowchart TD
A[User Requests] --> B[Load Balancer]
B --> C[Server 1]
B --> D[Server 2]
B --> E[Server 3]
C --> F[Database Cluster]
D --> F
E --> F
style A fill:#FF8000,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style B fill:#4DA6FF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style C fill:#4DFFB8,stroke:#fff,color:#333
style D fill:#4DFFB8,stroke:#fff,color:#333
style E fill:#4DFFB8,stroke:#fff,color:#333
style F fill:#A64DFF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
Redundancy Systems
Duplicate components and systems that can take over if primary systems fail, including backup servers, alternate network paths, and mirrored data centers.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Documented procedures for restoring systems after major disruptions, with defined recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO).
Load Balancing
Distribution of workloads across multiple computing resources to optimize resource use, maximize throughput, and ensure high availability.
When I work with healthcare organizations, where system availability can literally be a matter of life and death, I use PageOn.ai to design comprehensive availability monitoring dashboards. These visual tools allow IT teams to quickly identify potential bottlenecks and vulnerabilities before they impact critical services.
By visualizing system dependencies and potential failure points, we can create more robust availability strategies that account for both technical and organizational factors. This approach has helped many organizations achieve their uptime goals while optimizing resource allocation and prioritizing the most critical systems.
Balancing the Triad: Finding Your Organization's Equilibrium
One of the most challenging aspects of implementing the CIA triad is finding the right balance between the three principles. In my experience, there's no one-size-fits-all approach—each organization must determine its own equilibrium based on its specific needs, industry requirements, and risk tolerance.
Security Trade-off Visualization
A comparative view of how different industries balance the CIA triad components:
Industry-Specific CIA Implementations
| Industry | Confidentiality Focus | Integrity Focus | Availability Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Patient records, HIPAA compliance | Medical data accuracy, treatment records | Critical care systems, patient portals |
| Financial Services | Customer financial data, transactions | Transaction accuracy, audit trails | Payment systems, trading platforms |
| E-commerce | Payment information, customer profiles | Inventory data, pricing information | Website uptime, checkout process |
| Manufacturing | Proprietary designs, supply chain data | Production specifications, quality data | Production systems, supply chain management |
Decision Framework for Security Investments
CIA Triad Decision Framework
A decision tree for evaluating security investments based on CIA priorities:
flowchart TD
A[Security Investment Decision] --> B{Primary Security Concern?}
B -->|Sensitive Data Protection| C[Focus on Confidentiality]
B -->|Data Accuracy & Trust| D[Focus on Integrity]
B -->|System Uptime & Access| E[Focus on Availability]
C --> F{Regulatory Requirements?}
D --> G{Financial or Safety Impact?}
E --> H{Business Continuity Needs?}
F -->|High| I[Encryption & Access Controls]
F -->|Low| J[Basic Protection Measures]
G -->|High| K[Advanced Verification Systems]
G -->|Low| L[Standard Integrity Checks]
H -->|Critical| M[Redundant Systems & DR]
H -->|Standard| N[Basic Availability Measures]
style A fill:#FF8000,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style C fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style D fill:#A64DFF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style E fill:#4DA6FF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style I fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style K fill:#A64DFF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style M fill:#4DA6FF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
I've worked with organizations across various industries to help them find their optimal security balance. Using PageOn.ai's Deep Search capabilities, we can create customized security balance visualizations that incorporate relevant industry benchmarks and best practices.
These visualizations help security teams and executives make more informed decisions about where to allocate resources and how to address specific risks. By clearly showing the trade-offs between different security priorities, we can develop more balanced and effective security strategies that align with business objectives while providing adequate protection.
Implementing the CIA Triad in Modern Security Architectures
Implementing the CIA triad in today's complex digital environments requires a thoughtful, layered approach. I've found that successful implementations integrate these principles into every aspect of the security architecture, from policy development to technical controls and user training.
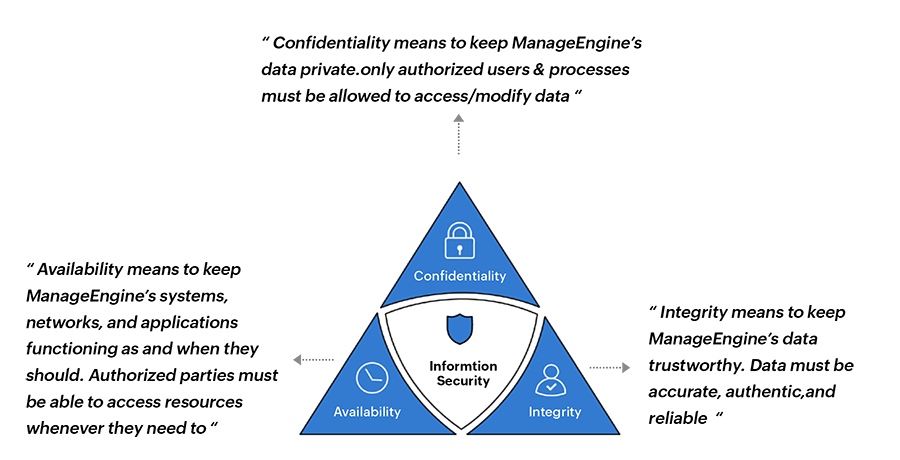
Mapping to Contemporary Security Challenges
Modern security architectures must address challenges like cloud computing, mobile devices, IoT, and increasingly sophisticated technology industry insights on threats. The CIA triad provides a framework for evaluating how these technologies impact security and what controls are needed to mitigate risks.
Threat Model Visualization
A visual representation of threats against each CIA pillar:
flowchart TD
A[Security Threats] --> B[Confidentiality Threats]
A --> C[Integrity Threats]
A --> D[Availability Threats]
B --> B1[Data Breaches]
B --> B2[Insider Threats]
B --> B3[Man-in-the-Middle]
B --> B4[Eavesdropping]
C --> C1[Data Tampering]
C --> C2[SQL Injection]
C --> C3[XSS Attacks]
C --> C4[Unauthorized Changes]
D --> D1[DDoS Attacks]
D --> D2[Hardware Failures]
D --> D3[Natural Disasters]
D --> D4[Resource Exhaustion]
style A fill:#FF8000,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style B fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style C fill:#A64DFF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style D fill:#4DA6FF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
Integration with Other Security Frameworks
The CIA triad doesn't exist in isolation—it complements and integrates with other security frameworks like NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO 27001. By mapping these frameworks together, organizations can create more comprehensive security programs that address both high-level principles and specific control requirements.
Framework Integration Comparison
How different security frameworks align with the CIA triad:
I've helped organizations implement the CIA triad by using PageOn.ai to transform complex security policies into clear visual guides. These visuals make security concepts more accessible and help employees understand how their actions impact the organization's overall security posture.
For example, when working with a manufacturing company that was concerned about intellectual property protection, we created visual workflows showing how different security controls protected their designs throughout the product development lifecycle. This approach helped both technical and non-technical staff understand the importance of following security procedures.
By integrating AI agent tool chains into these visual guides, organizations can automate security monitoring and response while maintaining human oversight of critical decisions. This balance of automation and human judgment is essential for maintaining security in increasingly complex environments.
Measuring CIA Triad Effectiveness
To ensure that your CIA triad implementation is working effectively, you need clear metrics and monitoring systems. In my experience, what gets measured gets managed—and security is no exception. By establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) for each pillar, you can track progress, identify gaps, and continuously improve your security posture.
Key Performance Indicators for Each Pillar
Confidentiality Metrics
- Access control violation incidents
- Data classification compliance rate
- Encryption coverage percentage
- Security awareness training completion
- DLP policy violation frequency
Integrity Metrics
- Data corruption incidents
- Change management compliance
- Backup verification success rate
- Input validation error frequency
- Code signing compliance
Availability Metrics
- System uptime percentage
- Mean time to recovery (MTTR)
- Successful DR test completions
- Service level agreement compliance
- Resource utilization trends
Security Posture Assessment
A sample security scorecard showing metrics across the CIA triad:
Turning Metrics into Actionable Insights
Collecting metrics is just the first step—the real value comes from analyzing this data to drive security improvements. I've found that visual dashboards are particularly effective for helping security teams identify patterns and prioritize their efforts.
For example, when working with a financial services client, we used PageOn.ai to create dynamic security scorecards that evolved with their threat landscape. These visualizations helped them track their progress over time and adjust their security investments based on changing risks and vulnerabilities.
Security Metrics Analysis Process
A flowchart showing how to turn security metrics into actionable improvements:
flowchart TD
A[Collect Security Metrics] --> B[Analyze Trends & Patterns]
B --> C[Identify Security Gaps]
C --> D[Prioritize Based on Risk]
D --> E[Implement Improvements]
E --> F[Measure Results]
F --> A
style A fill:#FF8000,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style C fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style E fill:#4DFFB8,stroke:#fff,color:#333
By leveraging PageOn.ai's visualization capabilities, security teams can transform complex security data into clear, actionable insights that drive continuous improvement. These visualizations help bridge the gap between technical security metrics and business objectives, making it easier to demonstrate the value of security investments to executives and stakeholders.
The Future of the CIA Triad
While the core principles of the CIA triad remain relevant, the security landscape continues to evolve rapidly. New technologies, threat vectors, and business models are challenging traditional security approaches and requiring us to adapt how we implement these principles.

Emerging Challenges to Traditional Security Models
Several trends are reshaping how we think about and implement the CIA triad in modern environments:
- Zero Trust Architecture: Moving beyond perimeter-based security to continuous verification of every access request, regardless of source.
- AI and Machine Learning: Both as security tools and as potential threat vectors through adversarial attacks.
- Quantum Computing: Potential to break current encryption standards, requiring new approaches to confidentiality.
- Decentralized Systems: Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies changing how we think about integrity and trust.
- Privacy Regulations: GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations adding compliance dimensions to confidentiality requirements.
Adaptation for Modern Computing Environments
CIA Triad Evolution for New Technologies
How the CIA triad is adapting to different technology environments:
Visual Forecasting of Security Trends
As security professionals, we need to anticipate how threats and technologies will evolve. The US-China AI race is just one example of how geopolitical factors are influencing the development of technologies that will shape future security landscapes.
Future Security Scenario Planning
A visualization of how different security scenarios might unfold:
flowchart TD
A[Current Security Landscape] --> B[Scenario 1: Increased Regulation]
A --> C[Scenario 2: AI-Driven Threats]
A --> D[Scenario 3: Quantum Breakthrough]
B --> B1[Enhanced Privacy Controls]
B --> B2[Standardized Security Frameworks]
B --> B3[Increased Compliance Costs]
C --> C1[Automated Attack Systems]
C --> C2[AI-Powered Defense]
C --> C3[Speed-Based Security Race]
D --> D1[Obsolete Encryption]
D --> D2[Post-Quantum Cryptography]
D --> D3[Quantum-Secure Networks]
style A fill:#FF8000,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style B fill:#4DA6FF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style C fill:#FF4D4D,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
style D fill:#A64DFF,stroke:#fff,color:#fff
Using PageOn.ai's scenario planning capabilities, security teams can create visual forecasts of how different trends might impact their security requirements. These visualizations help organizations prepare for multiple possible futures and develop more adaptable security strategies.
As we look to the future, the CIA triad will continue to provide a valuable framework for thinking about security, even as the specific implementation details evolve. By focusing on the core principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability—while adapting our approaches to new technologies and threats—we can build security programs that remain effective in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Transform Your Security Visualizations with PageOn.ai
Ready to bring your cybersecurity concepts to life with clear, compelling visuals? PageOn.ai makes it easy to create professional-grade security diagrams, dashboards, and training materials that help your team understand and implement the CIA triad effectively.
Conclusion: Building a Secure Future with the CIA Triad
Throughout this guide, I've explored how the CIA triad serves as a foundational framework for cybersecurity, providing a structured approach to protecting information assets across organizations of all sizes and industries. From its historical roots to its future applications, the triad continues to offer valuable guidance for security professionals navigating an increasingly complex threat landscape.
As I've shown, visualizing security concepts is a powerful way to improve understanding and implementation. Clear visual representations help bridge the gap between technical security requirements and business objectives, making it easier to communicate security needs and gain support for necessary investments.
The evolution of American infrastructure from physical to digital systems has created new security challenges that require innovative approaches. By applying the CIA triad principles with modern visualization tools like PageOn.ai, organizations can develop more effective security strategies that adapt to changing technologies and threats.
As you work to strengthen your organization's security posture, remember that the CIA triad isn't just a theoretical model—it's a practical framework for making security decisions that protect your most valuable assets while enabling your business to thrive. By finding the right balance between confidentiality, integrity, and availability for your specific needs, you can build a security program that's both effective and sustainable in the face of evolving challenges.
You Might Also Like
First Principles Framework for Building Powerful AI Commands | Master AI Prompt Engineering
Learn the first principles approach to crafting powerful AI commands. Master prompt engineering with proven frameworks, templates, and visualization techniques for optimal AI interaction.
Prompt Chaining Techniques That Scale Your Business Intelligence | Advanced AI Strategies
Master prompt chaining techniques to transform complex business intelligence workflows into scalable, automated insights. Learn strategic AI methodologies for data analysis.
The AI Superpower Timeline: Visualizing US-China AI Race & Tech Developments
Explore the narrowing US-China AI performance gap, historical milestones, technical battlegrounds, and future projections in the global artificial intelligence race through interactive visualizations.
Unleashing the Power of Agentic Workflows: Visual Clarity for Complex AI Processes
Discover how to transform complex agentic workflows into clear visual representations. Learn to design, implement and optimize AI agent processes with PageOn's visualization tools.
