Democratizing AI Agents: How Non-Technical Users Can Create Powerful Automated Solutions
Understanding AI Agents for the Non-Technical Creator
The world of AI agents is undergoing a fundamental transformation, moving from complex coding requirements to intuitive visual interfaces that anyone can use. I've witnessed this shift firsthand and am excited to share how non-technical users like you can now create sophisticated AI agents that automate tasks, enhance productivity, and drive business value—all without writing a single line of code.
Understanding AI Agents for the Non-Technical Creator
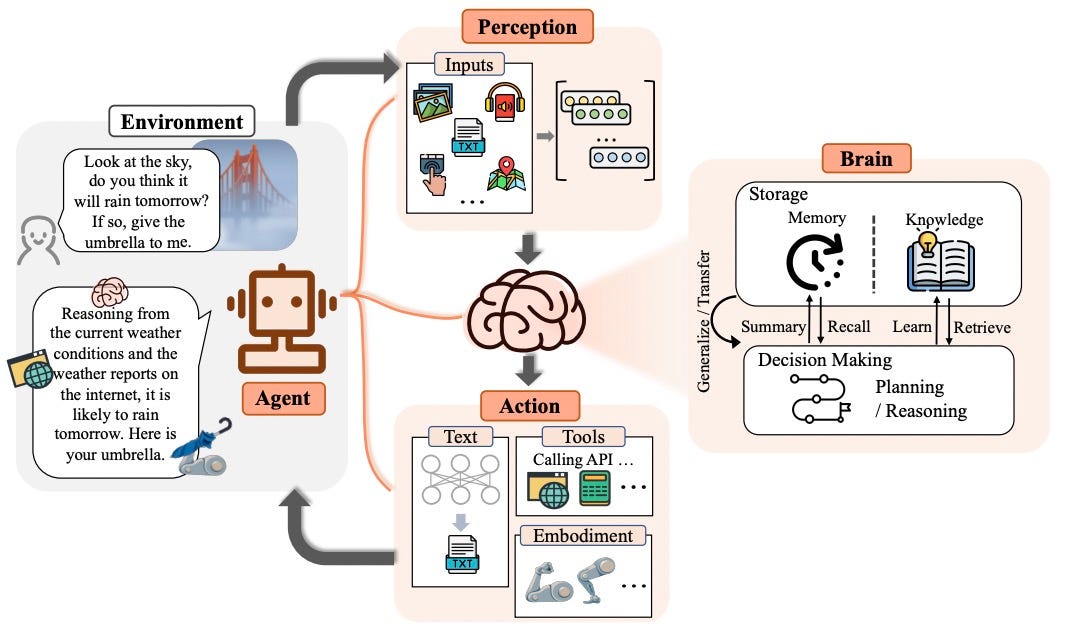
I remember when creating AI agents required extensive programming knowledge, making it inaccessible to most business users. Today, we're witnessing a fundamental shift from code-dependent to visual AI agent creation, democratizing this powerful technology.
What Makes an AI Agent Valuable?
For everyday business users, a valuable AI agent is one that can autonomously perform specific tasks based on instructions, learn from interactions, and integrate with existing tools. Unlike static chatbots, true AI agents can make decisions, take actions, and adapt to new scenarios.
Key Differences Between AI Agents and Traditional Tools
| Feature | Traditional Automation | Simple Chatbots | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Rule-based only | Limited pattern matching | Contextual understanding |
| Adaptability | None | Minimal | Learns from interactions |
| Creation Complexity | Moderate | Simple to moderate | Now accessible with visual tools |
Breaking the Technical Barrier
Many people believe AI agent creation requires technical expertise—a psychological barrier that's rapidly disappearing. In reality, modern platforms have abstracted away the complexity, allowing business users to focus on what matters: solving real problems with AI.
Benefits of AI Agents for Non-Technical Teams
The Evolution of No-Code AI Agent Platforms
I've watched with fascination as visual builders have revolutionized the AI landscape, making technology previously reserved for developers accessible to everyone. This evolution represents a significant democratization of AI capabilities.
Popular No-Code AI Agent Platforms
Several platforms have emerged as leaders in the no-code AI agent space, each with unique strengths. Platforms like Lindy offer guided workflows specifically designed for non-technical users, while others like Zapier and Make leverage their existing automation ecosystems to incorporate AI capabilities.
How Visual Interfaces Transform Complex Logic
flowchart TD
A[Business Problem] --> B[Visual Workflow Designer]
B --> C{Decision Point}
C -->|Condition 1| D[Action 1]
C -->|Condition 2| E[Action 2]
D --> F[Integration with External Tools]
E --> F
F --> G[Automated Outcome]
style A fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style B fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style C fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style D fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style E fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style F fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
style G fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
The User-Centric Shift
The shift from developer-centric to user-centric AI agent creation tools represents a fundamental change in how we think about technology development. By focusing on intuitive interfaces and visual workflows, these platforms enable users to conceptualize agent behaviors without getting lost in technical details.
Platform Comparison: Technical Expertise Required
Essential Components of User-Friendly AI Agent Builders
In my experience working with various AI agent platforms, I've identified several critical components that make these tools truly accessible to non-technical users. These elements bridge the gap between complex AI capabilities and intuitive user experiences.
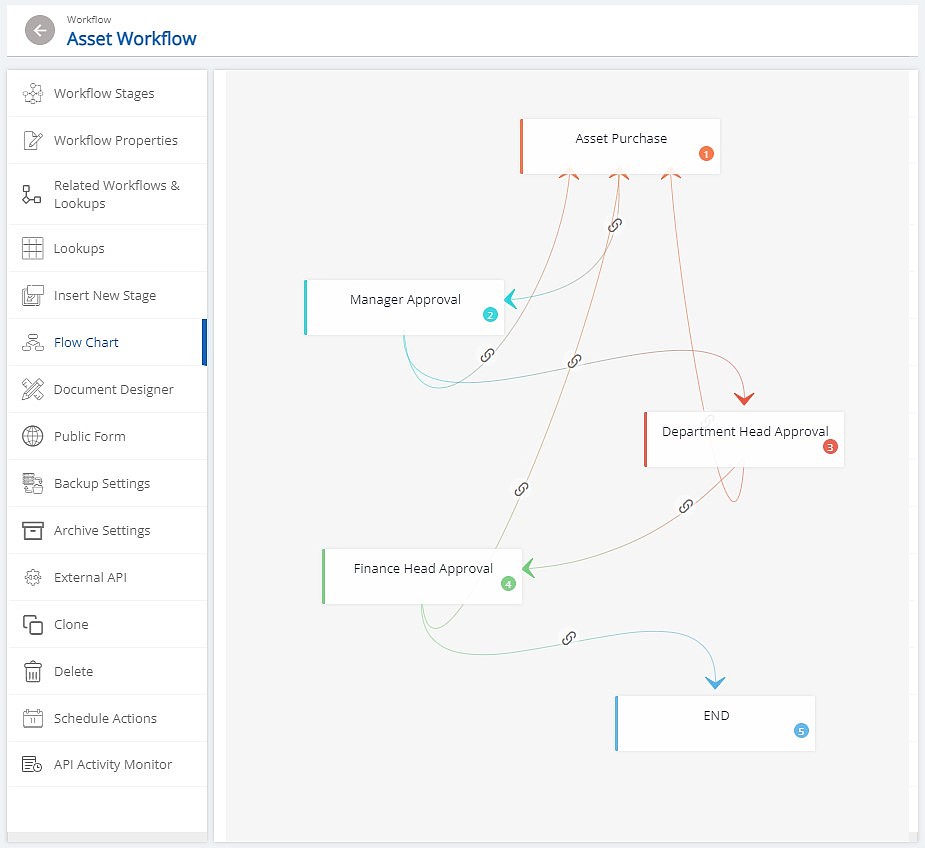
Visual Workflow Designers
The heart of any no-code AI agent platform is its visual workflow designer. These interfaces allow users to map out agent behaviors through intuitive drag-and-drop elements, connecting triggers, actions, and decision points without writing code. AI agent tool chains create powerful workflows through this visual design approach, making complex logic accessible.
Components of a No-Code AI Agent Builder
flowchart TB
A[No-Code AI Agent Builder] --> B[Visual Workflow Designer]
A --> C[Pre-built Templates]
A --> D[Natural Language Instructions]
A --> E[Integration Hub]
A --> F[Testing Environment]
B --> G[Drag & Drop Interface]
B --> H[Decision Nodes]
B --> I[Action Blocks]
C --> J[Industry-Specific Templates]
C --> K[Function-Based Templates]
D --> L[Prompt Engineering Interface]
D --> M[Context Management]
E --> N[API Connections]
E --> O[Third-Party Services]
F --> P[Simulation Tools]
F --> Q[Debugging Assistance]
style A fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style C fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style D fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style E fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style F fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
Pre-built Templates
Templates serve as invaluable starting points, especially for newcomers to AI agent creation. Rather than beginning with a blank canvas, users can select from pre-built templates designed for specific business functions like customer support, lead qualification, or content management.
Natural Language Instructions
One of the most significant advancements is the ability to guide AI agents using natural language rather than programming languages. This approach allows business users to communicate their requirements in familiar terms, specifying what they want the agent to accomplish without technical syntax.
Natural Language vs. Programming Language
Natural Language Instruction
"When a customer submits a support ticket about billing, categorize it as 'Finance', assign it to the Finance team, and send an automated acknowledgment email with estimated response time."
Programming Equivalent
if (ticket.content.includes("billing") ||
ticket.content.includes("payment") ||
ticket.content.includes("invoice")) {
ticket.category = "Finance";
ticket.assignTo(teams.finance);
sendEmail(ticket.customer.email,
templates.acknowledgment,
{responseTime: "24 hours"});
}
Integration Capabilities
For AI agents to be truly useful in business contexts, they must seamlessly connect with existing tools and platforms. The best no-code builders offer extensive integration capabilities, allowing agents to interact with CRM systems, email platforms, document storage, and other business-critical applications.
Practical Applications Across Business Functions
I've seen AI agents transform operations across various business departments. Here are some practical applications that non-technical users can implement using today's visual AI agent builders.
Sales & Marketing Applications

In sales and marketing, AI agents can qualify leads, nurture prospects, and distribute content based on engagement patterns. By leveraging ai content creation capabilities within agent workflows, teams can automate personalized outreach at scale.
Example: Lead Qualification Agent
A marketing team created a lead qualification agent that:
- Analyzes incoming form submissions and website behavior
- Scores leads based on predefined criteria
- Automatically routes high-value prospects to sales representatives
- Enrolls other leads in appropriate nurturing sequences
- Generates personalized follow-up content based on prospect interests
Using PageOn.ai's Deep Search, this agent can integrate customer data from multiple sources to provide comprehensive context in its responses.
Customer Support Scenarios
Customer Support Ticket Triage Workflow
flowchart TD
A[Customer Submits Ticket] --> B{Analyze Content}
B -->|Technical Issue| C[Route to Tech Support]
B -->|Billing Question| D[Route to Finance]
B -->|Product Inquiry| E[Route to Sales]
B -->|General Question| F[Route to General Support]
C --> G[Generate Technical Response Template]
D --> H[Access Billing Records]
E --> I[Prepare Product Information]
F --> J[Search Knowledge Base]
G --> K[Send Response with Visual Solution]
H --> L[Respond with Account Details]
I --> M[Respond with Product Recommendations]
J --> N[Respond with Relevant Articles]
style A fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style B fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style C fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style D fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style E fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style F fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style K fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
style L fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
style M fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
style N fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
Customer support teams can benefit tremendously from AI agents that triage tickets, generate responses for common inquiries, and create visual explanations of solutions. These agents can analyze incoming requests, categorize them by topic and urgency, and route them to the appropriate department.
Example: Knowledge Base Assistant
A support team built an agent that:
- Monitors customer questions across multiple channels
- Searches the knowledge base for relevant articles
- Extracts the most pertinent information
- Generates visual explanations using PageOn.ai's AI Blocks
- Delivers personalized responses with step-by-step visual guides
This approach has reduced resolution time by 45% and improved customer satisfaction scores.
Operational Efficiency

Operations teams can leverage AI agents for meeting scheduling, document processing, and information extraction. These agents can automate routine tasks, ensuring consistency and reducing the time spent on manual processes.
Time Saved by Function with AI Agents
Example: Document Processing Agent
An operations team created an agent that:
- Monitors shared inboxes for incoming documents
- Extracts key information from invoices, contracts, and forms
- Categorizes and files documents in the appropriate storage location
- Updates relevant database records with extracted information
- Visualizes complex operational processes using PageOn.ai's visual structures
This agent reduced document processing time by 85% and virtually eliminated data entry errors.
Best Practices for Creating Effective AI Agents Without Coding
Through my experience helping teams implement AI agents, I've developed a set of best practices that ensure success, even for those with no technical background.

Start with Clear Goals
The most successful AI agent implementations begin with clearly defined goals and specific use cases. Rather than creating an agent that attempts to solve multiple complex problems, focus on a single, well-defined task or workflow. This approach allows you to refine the agent's performance and expand its capabilities over time.
Write Effective Prompts
The quality of your AI agent's performance depends significantly on how well you communicate your requirements. Learning to write effective AI prompts is essential for guiding agent behavior. Clear, specific instructions with examples yield better results than vague directives.
Prompt Writing Examples
Ineffective Prompt
"Reply to customer emails about problems."
Too vague, provides no guidance on tone, structure, or specific scenarios.
Effective Prompt
"When responding to customer support emails about product issues, first acknowledge their frustration, then ask clarifying questions if needed. If you can identify the solution, provide step-by-step instructions with a friendly, helpful tone. Always end with an offer for further assistance."
Specific, includes tone guidance, structure, and clear expectations.
Testing and Iteration
AI agent development is inherently iterative. I always recommend testing your agent with various scenarios, including edge cases, and refining its behavior based on the results. Most no-code platforms include testing environments that allow you to simulate interactions before deploying the agent to production.
AI Agent Testing and Iteration Cycle
flowchart LR
A[Design Initial Agent] --> B[Test with Sample Data]
B --> C{Performance Acceptable?}
C -->|No| D[Refine Prompts & Logic]
D --> B
C -->|Yes| E[Limited Deployment]
E --> F[Gather User Feedback]
F --> G{Improvements Needed?}
G -->|Yes| H[Implement Changes]
H --> E
G -->|No| I[Full Deployment]
style A fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style B fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style C fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style D fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style E fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style F fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style G fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style H fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style I fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
Building in Guardrails
Even without programming knowledge, you can implement effective guardrails to ensure your AI agent operates within appropriate boundaries. These safeguards might include approval workflows for certain actions, confidence thresholds for automated responses, or specific scenarios where the agent should escalate to a human.
Ensuring Consistent Communication Style
Using PageOn.ai's Vibe Creation feature, you can ensure your agents communicate in a consistent tone and style that aligns with your brand voice. This helps create a seamless experience for users interacting with both human team members and AI agents.
Overcoming Common Challenges for Non-Technical Agent Creators
Creating AI agents without technical expertise presents unique challenges. Here's how I've helped teams overcome the most common obstacles.

Handling Complex Decision Trees
Decision trees can quickly become complex, even for relatively straightforward agent workflows. Without coding knowledge, this complexity can be overwhelming. The solution lies in breaking down large decision trees into smaller, manageable components and using visual tools to map out the logic.
Breaking Down Complex Decision Trees
flowchart TD
A[Complex Problem] --> B[Modular Approach]
B --> C[Module 1: Initial Assessment]
B --> D[Module 2: Data Processing]
B --> E[Module 3: Decision Making]
B --> F[Module 4: Action Execution]
C --> G{Assessment Complete?}
G -->|Yes| D
G -->|No| H[Request More Information]
H --> C
style A fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style B fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style C fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style D fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style E fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style F fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style G fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style H fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
Managing Agent Memory and Context
Without database expertise, managing an agent's memory and maintaining context across interactions can be challenging. Modern no-code platforms address this by providing built-in memory management features that handle the technical aspects of storing and retrieving information.
Memory Management Strategies
- Session Memory: Information retained during a single conversation
- Long-term Memory: Historical data stored across multiple interactions
- External Knowledge: Integration with databases and knowledge bases
- Memory Summarization: Condensing important information to maintain context
Modern no-code platforms handle these memory types automatically, allowing non-technical users to focus on agent behavior rather than data storage mechanics.
Troubleshooting Agent Behavior
When an agent doesn't behave as expected, troubleshooting can be intimidating without debugging skills. The key is to use the visualization tools available in no-code platforms to understand the agent's decision path and identify where issues occur.
PageOn.ai's AI Blocks feature is particularly valuable for visualizing agent logic and workflows, making it easier to identify and address problems. By creating visual representations of the agent's decision-making process, non-technical users can better understand and refine its behavior.
Scaling Agent Capabilities
As your comfort with AI agent creation grows, you'll likely want to expand your agent's capabilities. The most effective approach is incremental development—adding new features one at a time and thoroughly testing each addition before moving on to the next enhancement.
Scaling Agent Complexity Over Time
Future of AI Agent Creation for Non-Technical Users
The landscape of AI agent creation is evolving rapidly, with exciting developments on the horizon that will make these tools even more accessible and powerful for non-technical users.

Emerging Visual Tools
The next generation of visual tools for AI agent creation promises even greater simplicity and power. We're seeing the emergence of platforms that combine the intuitive nature of visual programming with the intelligence of AI assistance, helping users design more sophisticated agents without increasing complexity.
Evolution of AI Agent Creation Interfaces
flowchart LR
A[Code-Based Development] --> B[Visual Programming]
B --> C[Natural Language Instructions]
C --> D[AI-Assisted Design]
D --> E[Autonomous Agent Creation]
style A fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style B fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style C fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style D fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style E fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
Specialized AI Assistants
We're witnessing the growth of an ecosystem of specialized AI assistants designed for specific industries and use cases. These purpose-built agents come with pre-configured capabilities tailored to particular domains, further reducing the barrier to entry for non-technical users.
Natural Language Interfaces
Perhaps the most transformative development is the evolution of natural language interfaces for agent creation. Soon, users will be able to describe the agent they want to build in conversational language, and AI will generate the appropriate workflows and logic automatically. This approach will make AI agent creation accessible to virtually anyone.
Example: Natural Language Agent Creation
"Create an agent that monitors our support inbox, categorizes tickets by urgency based on keywords, and assigns them to the appropriate department. For urgent issues, it should send an immediate notification to the on-call team."
The system would automatically translate this description into a functional agent with appropriate triggers, conditions, and actions.
Visualizing Abstract Concepts
PageOn.ai is at the forefront of transforming abstract agent concepts into visual workflows. By providing intuitive visualization tools, PageOn.ai makes it easier for non-technical users to understand and design complex agent behaviors. This visual approach to agent creation will become increasingly important as agents take on more sophisticated roles.
Non-Technical Users as Primary Creators
Perhaps the most significant shift on the horizon is the potential for non-technical users to become the primary creators of business AI solutions. As tools become more accessible and powerful, domain experts—rather than developers—will lead the charge in designing AI agents that address specific business challenges.
Projected Growth in Non-Technical AI Agent Creators
Getting Started: Your First AI Agent Without Writing Code
Ready to create your first AI agent? I'll walk you through the process of getting started, even if you have no technical background.

Selecting the Right Platform
The first step is choosing a no-code platform that aligns with your specific needs and experience level. Consider factors like the platform's user interface, available templates, integration capabilities, and support resources.
Platform Selection Criteria
- Ease of Use: Look for intuitive interfaces with minimal learning curve
- Templates: Availability of pre-built templates for your specific use case
- Integrations: Compatibility with your existing tools and platforms
- Support Resources: Documentation, tutorials, and community forums
- Pricing: Cost structure that aligns with your budget and expected usage
For beginners, platforms like Lindy, Zapier, or Make offer guided experiences with extensive templates and support resources.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your First Agent
First Agent Creation Process
flowchart TD
A[Define Your Goal] --> B[Select a Template]
B --> C[Customize Trigger Events]
C --> D[Configure Decision Points]
D --> E[Set Up Actions]
E --> F[Test With Sample Data]
F --> G{Working as Expected?}
G -->|No| H[Refine Configuration]
H --> F
G -->|Yes| I[Deploy Your Agent]
style A fill:#FFE5CC,stroke:#FF8000
style B fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style C fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style D fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style E fill:#FFB366,stroke:#FF8000
style F fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style G fill:#FF9A3C,stroke:#FF8000
style H fill:#FFCC99,stroke:#FF8000
style I fill:#FF8000,stroke:#FF8000
-
Define a Specific Goal:
Start with a clear, focused objective for your agent. For example, "Categorize incoming support tickets and route them to the appropriate department."
-
Select a Template:
Most platforms offer templates for common use cases. Choose one that closely matches your goal to give yourself a head start.
-
Customize Trigger Events:
Define what will activate your agent. This might be an incoming email, a form submission, a calendar event, or a scheduled time.
-
Configure Decision Points:
Set up the logic that will guide your agent's behavior. For example, "If the email contains 'billing' in the subject, route to the finance team."
-
Set Up Actions:
Define what your agent will do based on its decisions. This might include sending emails, updating records, or notifying team members.
-
Test Thoroughly:
Before deploying your agent, test it with various scenarios to ensure it behaves as expected.
-
Deploy and Monitor:
Once you're confident in your agent's performance, deploy it and monitor its behavior in real-world situations.
Essential Resources and Communities
You don't have to navigate the world of AI agent creation alone. Numerous resources and communities are available to support non-technical users:
- Platform-specific documentation and tutorials
- YouTube channels dedicated to no-code AI development
- Online forums and communities where users share tips and solutions
- Webinars and virtual workshops focused on AI agent creation
- Case studies of successful implementations by non-technical teams
Visualizing Your Agent's Workflow
Before implementing your agent, consider using PageOn.ai to visualize its workflow. Creating a visual representation of your agent's decision points and actions can help you identify potential issues and refine your approach before building.
Measuring Success and Iterating
Once your agent is deployed, establish clear metrics to measure its success. These might include time saved, error reduction, response time improvement, or user satisfaction. Use these metrics to guide your iteration process, continuously refining your agent to improve its performance.
Key Performance Metrics for AI Agents
Transform Your Visual Expressions with PageOn.ai
Ready to bring your AI agent workflows to life with stunning visualizations? PageOn.ai provides the tools you need to transform complex agent logic into clear, engaging visual expressions that anyone can understand—no technical expertise required.
Embracing the AI Agent Revolution
The democratization of AI agent creation represents a significant shift in how businesses leverage technology. By making these powerful tools accessible to non-technical users, we're unlocking new possibilities for innovation and efficiency across organizations of all sizes.
As we've explored throughout this guide, creating effective AI agents no longer requires coding expertise. With visual builders, intuitive interfaces, and supportive communities, anyone can design and deploy agents that automate tasks, enhance customer experiences, and drive business value.
I encourage you to take the first step in your AI agent journey. Start small, focus on a specific use case, and leverage the visualization capabilities of tools like PageOn.ai to bring your ideas to life. As your confidence grows, so too will the sophistication and impact of your AI agents.
The future of business automation is here, and it's accessible to everyone. Are you ready to join the revolution?
You Might Also Like
From Status Quo to Solution: Crafting the Perfect Pitch Narrative Arc | PageOn.ai
Learn how to transform your business presentations with powerful status quo to solution narratives. Discover visual storytelling techniques that captivate investors and stakeholders.
From Slides to Stories: Transform Presentations into Purpose-Driven Visual Experiences
Discover how to move beyond traditional PowerPoint presentations to create purpose-driven visual experiences that engage audiences, drive action, and leave lasting impact.
Audience-Centered Pitching Techniques: Visual Strategies That Win Every Time
Discover powerful audience-centered pitching techniques using visual storytelling, interactive engagement, and benefit visualization strategies that consistently win over any audience.
Transform Any Content into Professional Slides: The Ultimate Conversion Guide
Learn expert techniques for converting documents, presentations, and visual content into professional slides with this comprehensive guide to content format transformation.
